|
Development of low relative magnetic permeability GTA welds of SS 316L using nitrogen alloying for application in particle accelerators
Austenitic stainless steel is widely used in the construction of vacuum chambers for particle accelerators, and a strong candidate material for helium vessel of superconducting radiofrequency cavities of high energy high power particle accelerators. High magnetic permeability of its welds is one of the major limitations of austenitic stainless steels for applications in particle accelerators.
Highlights:
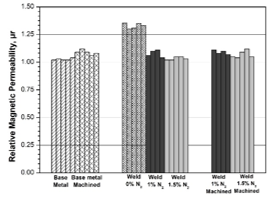
Gas tungsten arc welds of 316L stainless steel with relative magnetic permeability close to that of the base metal were produced using conventional ER 316L filler with addition of 1-1.5% nitrogen in the argon shielding gas (Fig.1). The resultant weld metal exhibited magnetic permeability (µr: 1.033–1.035) quite close to that of the base metal (µr :1.02–1.05).
There was a significant reduction in the FN value of weld metal from 4.53 (without nitrogen) to about 0.22–0.59 for the WM with a 1.5% nitrogen addition in the argon shield gas.
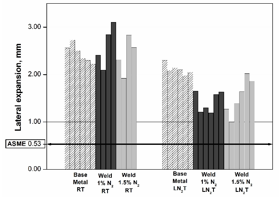
The welds displayed good strength and ductility and qualified the impact test requirements of Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code for operation at room temperature as well as at 4K liquid helium temperature. This technique can find important applications for the fabrication of ASME Code compliant 316L SS vacuum chambers and pressure vessels for particle accelerators, including helium vessel of superconducting RF cavities (Fig.2).
|
|
Fig. 1: Comparison of magnetic permeability of base metal and welded specimens (shield gas: Ar with 0%, 1% and 1.5% N2) in as welded and machined conditions. |
Fig. 2: Charpy impact test results (lateral expansion) with minimum qualifying value as specified by ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code. RT: Room-temperature; LN2T: Liquid nitrogen temperature. |
Publication: Development of Low-Magnetic-Permeability Welds of 316L Stainless Steel, Abhay Kumar etal, Oct. 2021, WELDING JOURNAL, Research supplement 323-s 33s.
Development of low magnetic permeability gas tungsten arc welds of AISI 316LN stainless steel (SS)
- Low magnetic permeability is an important selection criterion for the material of beam pipes & vacuum chambers of electron accelerators for minimizing distortion of the magnetic field.
- Material of construction of vacuum chamber of new 20 MeV/30 mA Injector Microtron for existing synchrotron radiation sources (Indus-1 & Indus-2): AISI 316 LN SS.
- Welding of 316LN SS with conventional filler alloys like ER316L and ER317L of AWS A5.9 produces duplex weld metal with 3–8% ferro-magnetic δ-ferrite to avoid solidification cracking.
Highlights:
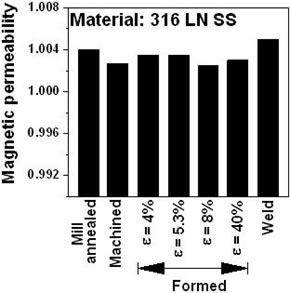
- GTAW of AISI 316LN SS with high Mn adaptation of W 18 16 5 N L filler produced a crack free low magnetic permeability weld (Fig.1) with acceptable mechanical properties.
- AISI 316LN SS is not required to be solution annealed after the final forming operation for obtaining low magnetic permeability (Fig.1), thereby avoiding solution annealing of large vacuum chamber in vacuum/controlled atmosphere furnace and associated problems of distortion.
- Besides Injector Microtron, the results provide useful input for design of future indigenous accelerators with vacuum chambers of austenitic SS.
|
Fig.1: Magnetic permeability of 316LN SS in different conditions. |
Publication: Abhay Kumar et al., Materials & Design, 53, 2014, 86-92.
|














